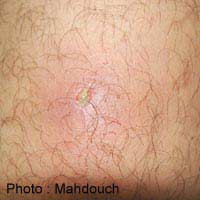
Folliculitis is a skin infection and inflammation of the hair follicles often caused by incorrect shaving techniques or improper hair removal. Folliculitis is also known as razor bumps and can develop into inflammation of the skin that is accompanied by the formation of pus and acne.
A Common Skin Disorder
Folliculitis is a common skin disorder that can affect men and women. Wherever hair grows on the body folliculitis can develop as it thrives on trapped bacteria that surrounds the hair follicle and appears as a white or red rash. Folliculitis can appear on the scalp, armpits, arms and legs and may even present as a rash on the face if a man shaves.
What Causes Folliculitis?
Blockage of the hair follicles causes attacks from bacteria and can also promote viruses and fungus, which increases the likelihood of folliculitis. A variety of other factors, that include excessive perspiration, friction and abrasions of the follicles, can also affect the skin in damaging ways. Acne and dermatitis create additional problems for the skin and can develop into folliculitis if not treated correctly and promptly.
Folliculitis Symptoms
Infected hair follicles develop into folliculitis and if left untreated the skin becomes red, tender and sore to the touch. Pus-filled swellings may also appear on the skin. The skin can also feel itchy and/or painful. Folliculitis can result from a single infected follicle, but generally this condition will affect many hair roots. Sometimes a crust forms on the skin’s surface and the infected hair will pierce the swelling.
How to Treat Folliculitis
Treatment of folliculitis depends on the location and severity of the infection. There are many different forms of folliculitis and these include Gram-negative Folliculitis, which is caused by long-term use of antibiotics, and Tinea barbae, which is caused by a fungus and appears as deep red pus-filled lumps anywhere on the body.
Most forms of folliculitis can be treated by a course of antibiotics and/or prescribed antifungal creams and ointments. Boils can be left to self-heal after the skin eruption has been drained of fluid by a GP or health practitioner. Prevention of further breakouts of folliculitis requires attention to washing and moisturisation techniques and regularity.
Folliculitis Prevention
In order to maintain a healthy hair regime it is important to use the best products and correct techniques. Washing the hair with gentle shampoo and conditioning removes the build up of sebum on the follicle and reduces the chances of trapped bacteria and blocked pores. When using depilatory creams or shaving it is important to cleanse and moisturise the skin correctly after hair removal takes place. Removing hair whilst the pores are open, after a hot shower for instance, is also advisable as it reduces stress to the hair follicles and prevents infection.
Allowing and encouraging the skin to breathe, by wearing loose clothing, also helps keep skin healthy and free from infection. Washing with antibacterial soap and ensuring the skin is well hydrated, by applying moisturiser and sunscreen, also keeps skin irritations and infections at bay.